Multimodal Retina Image Alignment and Applications
Team Members
Principal Investigators
Truong Q. Nguyen (PI) | William R. Freeman (Co-PI) | Dirk-Uwe Bartsch (Co-PI) | Cheolhong An (Co-PI)
Research Fellows
Melina Cavichini-Cordeiro | Fritz Gerald P. Kalaw | Manuel J. Amador-Patarroyo
Students
Major Goals
The objective of the project is to develop deep-learning based multimodal retinal image registration methods to help the ophthalmologist to quickly detect and diagnose retinal diseases. Four major goals: (1). Collect and prepare a wide range of retina images/data to support algorithm development and testing; (2). Develop algorithm to align ultra-widefield, color fundus and multicolor images to help with early diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases, (3). Develop segmentation algorithm for OCT volumes with the help of motion correction, and (4). Evaluate and assess the ability of goals 2 and 3 in diagnosis evaluation using human experts (clinical specialist).
Results (Publications)
2023
Ultra-wide field and new wide field composite retinal image registration with AI-enabled pipeline and 3D distortion correction algorithm
Fritz Gerald P. Kalaw, Melina Cavichini, Junkang Zhang, Bo Wen, Andrew C. Lin, Anna Heinke, Truong Nguyen, Cheolhong An, Dirk-Uwe G. Bartsch, Lingyun Cheng, William R. Freeman
Eye, 2023
[Paper (link)]
Abstract
This study aimed to compare a new Artificial Intelligence (AI) method to conventional mathematical warping in accurately overlaying peripheral retinal vessels from two different imaging devices: confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscope (cSLO) wide-field images and SLO ultra-wide field images. Images were captured using the Heidelberg Spectralis 55-degree field-of-view and Optos ultra-wide field. The conventional mathematical warping was performed using Random Sample Consensus—Sample and Consensus sets (RANSAC-SC). This was compared to an AI alignment algorithm based on a one-way forward registration procedure consisting of full Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) with Outlier Rejection (OR CNN), as well as an iterative 3D camera pose optimization process (OR CNN + Distortion Correction [DC]). Images were provided in a checkerboard pattern, and peripheral vessels were graded in four quadrants based on alignment to the adjacent box. A total of 660 boxes were analysed from 55 eyes. Dice scores were compared between the three methods (RANSAC-SC/OR CNN/OR CNN + DC): 0.3341/0.4665/4784 for fold 1-2 and 0.3315/0.4494/4596 for fold 2-1 in composite images. The images composed using the OR CNN + DC have a median rating of 4 (out of 5) versus 2 using RANSAC-SC. The odds of getting a higher grading level are 4.8 times higher using our OR CNN + DC than RANSAC-SC (p \\< 0.0001). Peripheral retinal vessel alignment performed better using our AI algorithm than RANSAC-SC. This may help improve co-localizing retinal anatomy and pathology with our algorithm.Accuracy and Time Comparison Between Side-by-Side and Artificial Intelligence Overlayed Images
Melina Cavichini, Dirk-Uwe G Bartsch, Alexandra Warter, Sumit Singh, Cheolhong An, Yiqian Wang, Junkang Zhang, Truong Nguyen, William R Freeman
Ophthalmic Surgery, Lasers and Imaging Retina, 2023
[Paper (link)]
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the accuracy and the time to find a lesion, taken in different platforms, color fundus photographs and infrared scanning laser ophthalmoscope images, using the traditional side-by-side (SBS) colocalization technique to an artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technique. Fifty-three pathological lesions were studied in 11 eyes. Images were aligned using SBS and AI overlaid methods. The location of each color fundus lesion on the corresponding infrared scanning laser ophthalmoscope image was analyzed twice, one time for each method, on different days, for two specialists, in random order. The outcomes for each method were measured and recorded by an independent observer. The colocalization AI method was superior to the conventional in accuracy and time (P \\< .001), with a mean time to colocalize 37\\% faster. The error rate using AI was 0\\% compared with 18\\% in SBS measurements. AI permitted a more accurate and faster colocalization of pathologic lesions than the conventional method.Accurate Registration between Ultra-Wide-Field and Narrow Angle Retina Images with 3D Eyeball Shape Optimization
Junkang Zhang, Bo Wen, Fritz Gerald P. Kalaw, Melina Cavichini, Dirk-Uwe G. Bartsch, William R. Freeman, Truong Q. Nguyen, Cheolhong An
2023 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), 2023
[Paper (link)]
Abstract
The Ultra-Wide-Field (UWF) retina images have attracted wide attentions in recent years in the study of retina. However, accurate registration between the UWF images and the other types of retina images could be challenging due to the distortion in the peripheral areas of an UWF image, which a 2D warping procedure can not handle. In this paper, we propose a novel 3D distortion correction method which sets up a 3D projection model and optimizes a dense 3D retina mesh to correct the distortion in the UWF image. The corrected UWF image can then be accurately aligned to the target image using 2D alignment methods. The experimental results show that our proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art method by 30\\%.2022
Self-Supervised Rigid Registration for Multimodal Retinal Images
Cheolhong An, Yiqian Wang, Junkang Zhang, Truong Q. Nguyen
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022
[Paper (link)]
Abstract
The ability to accurately overlay one modality retinal image to another is critical in ophthalmology. Our previous framework achieved the state-of-the-art results for multimodal retinal image registration. However, it requires human-annotated labels due to the supervised approach of the previous work. In this paper, we propose a self-supervised multimodal retina registration method to alleviate the burdens of time and expense to prepare for training data, that is, aiming to automatically register multimodal retinal images without any human annotations. Specially, we focus on registering color fundus images with infrared reflectance and fluorescein angiography images, and compare registration results with several conventional and supervised and unsupervised deep learning methods. From the experimental results, the proposed self-supervised framework achieves a comparable accuracy comparing to the state-of-the-art supervised learning method in terms of registration accuracy and Dice coefficient. 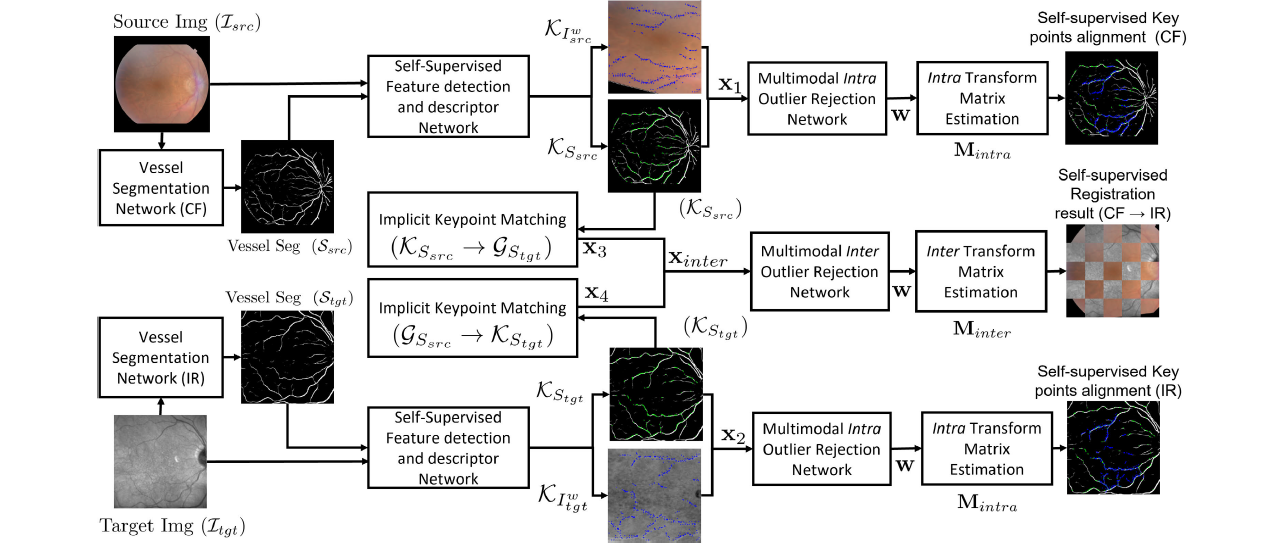
Two-Step Registration on Multi-Modal Retinal Images via Deep Neural Networks
Junkang Zhang, Yiqian Wang, Ji Dai, Melina Cavichini, Dirk-Uwe G. Bartsch, William R. Freeman, Truong Q. Nguyen, Cheolhong An
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022
[Paper (link)]
Abstract
Multi-modal retinal image registration plays an important role in the ophthalmological diagnosis process. The conventional methods lack robustness in aligning multi-modal images of various imaging qualities. Deep-learning methods have not been widely developed for this task, especially for the coarse-to-fine registration pipeline. To handle this task, we propose a two-step method based on deep convolutional networks, including a coarse alignment step and a fine alignment step. In the coarse alignment step, a global registration matrix is estimated by three sequentially connected networks for vessel segmentation, feature detection and description, and outlier rejection, respectively. In the fine alignment step, a deformable registration network is set up to find pixel-wise correspondence between a target image and a coarsely aligned image from the previous step to further improve the alignment accuracy. Particularly, an unsupervised learning framework is proposed to handle the difficulties of inconsistent modalities and lack of labeled training data for the fine alignment step. The proposed framework first changes multi-modal images into a same modality through modality transformers, and then adopts photometric consistency loss and smoothness loss to train the deformable registration network. The experimental results show that the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art results in Dice metrics and is more robust in challenging cases. 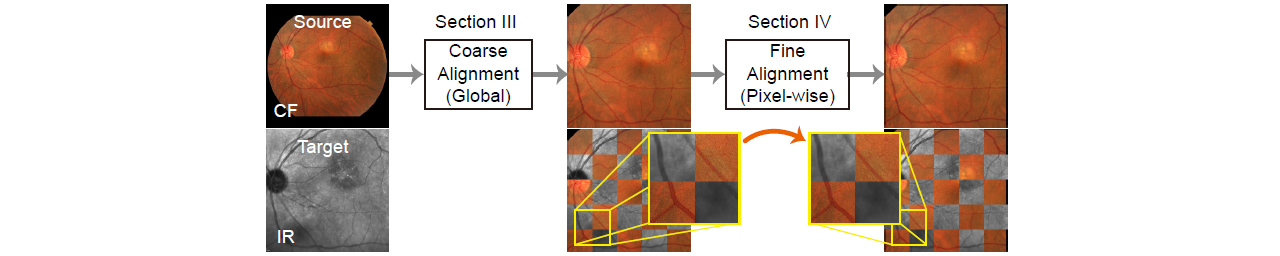
2021
Robust Content-Adaptive Global Registration for Multimodal Retinal Images Using Weakly Supervised Deep-Learning Framework
Yiqian Wang, Junkang Zhang, Melina Cavichini, Dirk-Uwe G. Bartsch, William R. Freeman, Truong Q. Nguyen, Cheolhong An
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021
[Paper (link)]
Abstract
Multimodal retinal imaging plays an important role in ophthalmology. We propose a content-adaptive multimodal retinal image registration method in this paper that focuses on the globally coarse alignment and includes three weakly supervised neural networks for vessel segmentation, feature detection and description, and outlier rejection. We apply the proposed framework to register color fundus images with infrared reflectance and fluorescein angiography images, and compare it with several conventional and deep learning methods. Our proposed framework demonstrates a significant improvement in robustness and accuracy reflected by a higher success rate and Dice coefficient compared with other methods. 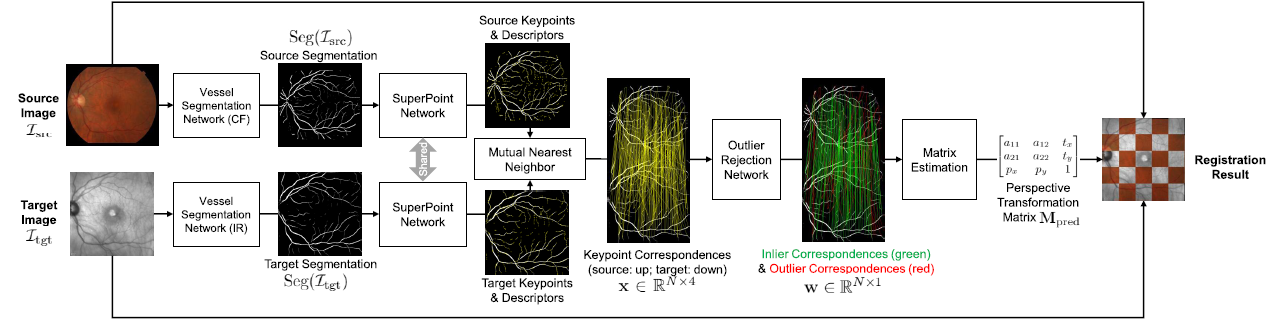
Perspective Distortion Correction for Multi-Modal Registration between Ultra-Widefield and Narrow-Angle Retinal Images
Junkang Zhang, Yiqian Wang, Dirk-Uwe G. Bartsch, William R. Freeman, Truong Q. Nguyen, Cheolhong An
2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), 2021
[Paper (link)]
Abstract
Multi-modal retinal image registration between 2D Ultra-Widefield (UWF) and narrow-angle (NA) images has not been well-studied, since most existing methods mainly focus on NA image alignment. The stereographic projection model used in UWF imaging causes strong distortions in peripheral areas, which leads to inferior alignment quality. We propose a distortion correction method that remaps the UWF images based on estimated camera view points of NA images. In addition, we set up a CNN-based registration pipeline for UWF and NA images, which consists of the distortion correction method and three networks for vessel segmentation, feature detection and matching, and outlier rejection. Experimental results on our collected dataset shows the effectiveness of the proposed pipeline and the distortion correction method. 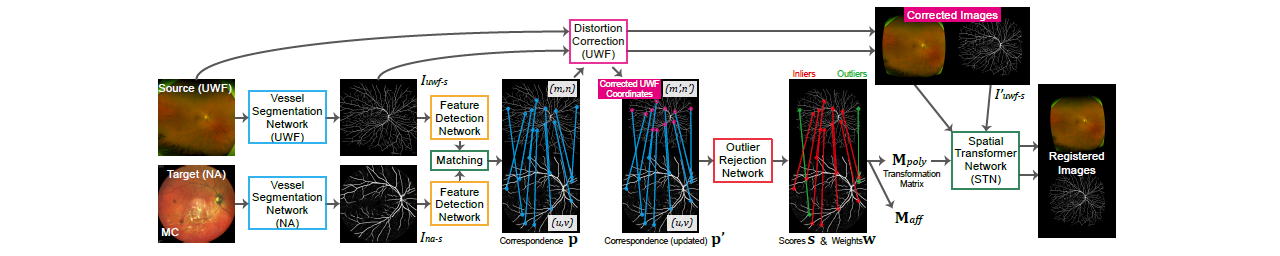
2020
Study on Correlation Between Subjective and Objective Metrics for Multimodal Retinal Image Registration
Yiqian Wang, Junkang Zhang, Melina Cavichini, Dirk-Uwe G. Bartsch, William R. Freeman, Truong Q. Nguyen, Cheolhong An
IEEE Access, 2020
[Paper (link)]
Abstract
Retinal imaging is crucial in diagnosing and treating retinal diseases, and multimodal retinal image registration constitutes a major advance in understanding retinal diseases. Despite the fact that many methods have been proposed for the registration task, the evaluation metrics for successful registration have not been thoroughly studied. In this article, we present a comprehensive overview of the existing evaluation metrics for multimodal retinal image registration, and compare the similarity between the subjective grade of ophthalmologists and various objective metrics. The Pearson's correlation coefficient and the corresponding confidence interval are used to evaluate metrics similarity. It is found that the binary and soft Dice coefficient on the segmented vessel can achieve the highest correlation with the subjective grades compared to other keypoint-supervised or unsupervised metrics. The paper established an objective metric that is highly correlated with the subjective evaluation of the ophthalmologists, which has never been studied before. The experimental results would build a connection between ophthalmology and image processing literature, and the findings may provide a good insight for researchers who investigate retinal image registration, retinal image segmentation and image domain transformation.Artificial Intelligence for Automated Overlay of Fundus Camera and Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscope Images
Melina Cavichini, Cheolhong An, Dirk-Uwe G. Bartsch, Mahima Jhingan, Manuel J. Amador-Patarroyo, Christopher P. Long, Junkang Zhang, Yiqian Wang, Alison X. Chan, Samantha Madala, Truong Nguyen, William R. Freeman
Translational Vision Science & Technology, 2020
[Paper (link)]
Abstract
{ The purpose of this study was to evaluate the ability to align two types of retinal images taken on different platforms; color fundus (CF) photographs and infrared scanning laser ophthalmoscope (IR SLO) images using mathematical warping and artificial intelligence (AI). We collected 109 matched pairs of CF and IR SLO images. An AI algorithm utilizing two separate networks was developed. A style transfer network (STN) was used to segment vessel structures. A registration network was used to align the segmented images to each. Neither network used a ground truth dataset. A conventional image warping algorithm was used as a control. Software displayed image pairs as a 5 × 5 checkerboard grid composed of alternating subimages. This technique permitted vessel alignment determination by human observers and 5 masked graders evaluated alignment by the AI and conventional warping in 25 fields for each image. Our new AI method was superior to conventional warping at generating vessel alignment as judged by masked human graders (P \\< 0.0001). The average number of good/excellent matches increased from 90.5\\% to 94.4\\% with AI method. AI permitted a more accurate overlay of CF and IR SLO images than conventional mathematical warping. This is a first step toward developing an AI that could allow overlay of all types of fundus images by utilizing vascular landmarks. The ability to align and overlay imaging data from multiple instruments and manufacturers will permit better analysis of this complex data helping understand disease and predict treatment. }A Segmentation Based Robust Deep Learning Framework for Multimodal Retinal Image Registration
Yiqian Wang, Junkang Zhang, Cheolhong An, Melina Cavichini, Mahima Jhingan, Manuel J. Amador-Patarroyo, Christopher P. Long, Dirk-Uwe G. Bartsch, William R. Freeman, Truong Q. Nguyen
ICASSP 2020 - 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 2020
[Paper (link)]
Abstract
Multimodal image registration plays an important role in diagnosing and treating ophthalmologic diseases. In this paper, a deep learning framework for multimodal retinal image registration is proposed. The framework consists of a segmentation network, feature detection and description network, and an outlier rejection network, which focuses only on the globally coarse alignment step using the perspective transformation. We apply the proposed framework to register color fundus images with infrared reflectance images and compare it with the state-of-the-art conventional and learning-based approaches. The proposed framework demonstrates a significant improvement in robustness and accuracy reflected by a higher success rate and Dice coefficient compared to other coarse alignment methods. 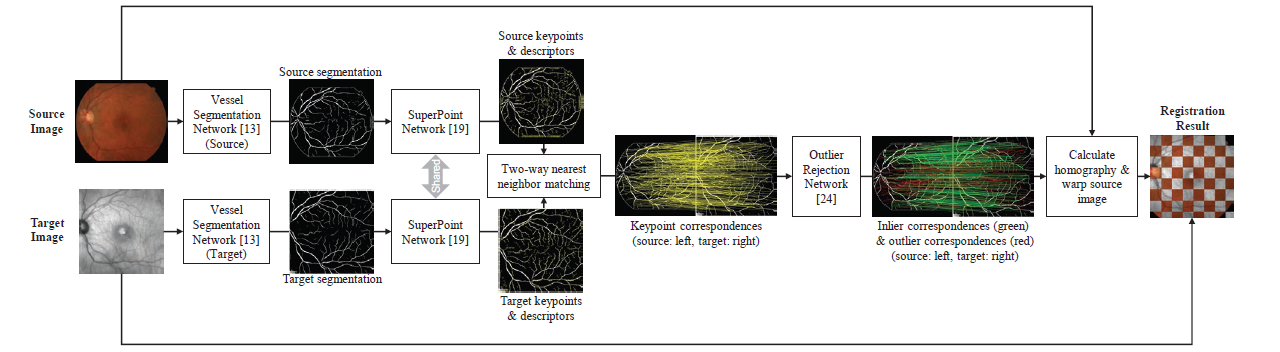
2019
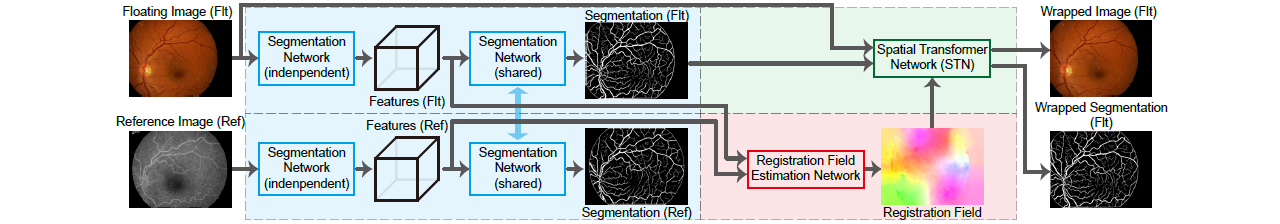
Joint Vessel Segmentation and Deformable Registration on Multi-Modal Retinal Images Based on Style Transfer
Junkang Zhang, Cheolhong An, Ji Dai, Manuel Amador, Dirk-Uwe Bartsch, Shyamanga Borooah, William R. Freeman, Truong Q. Nguyen
2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), 2019
[Paper (link)] [Supplementary] [Code]
Abstract
In multi-modal retinal image registration task, there are two major challenges, i.e., poor performance in finding correspondence due to inconsistent features, and lack of labeled data for training learning-based models. In this paper, we propose a joint vessel segmentation and deformable registration model based on CNN for this task, built under the framework of weakly supervised style transfer learning and perceptual loss. In vessel segmentation, a style loss guides the model to generate segmentation maps that look authentic, and helps transform images of different modalities into consistent representations. In deformable registration, a content loss helps find dense correspondence for multi-modal images based on their consistent representations, and improves the segmentation results simultaneously. Experiment results show that our model has better performance than other deformable registration methods in both quantitative and visual evaluations, and the segmentation results also help the rigid transformation1.